Scientific publications
Ahrazem O, Diretto G, Rambla JL, Rubio-Moraga Á, Lobato-Gómez M, Frusciante S, Argandoña J, Presa S, Granell A, Gómez-Gómez L (2022) Engineering high levels of saffron apocarotenoids in tomato. Horticulture Research 9: uhac074
Azariadis A, Vouligeas F, Salame E, Kouhen M, Rizou M, Blazakis K, Sotiriou P, Ezzat L, Mekkaoui K, Monzer A, et al (2023) Response of Prolyl 4 Hydroxylases, Arabinogalactan Proteins and Homogalacturonans in Four Olive Cultivars under Long-Term Salinity Stress in Relation to Physiological and Morphological Changes. Cells 12: 1466
Berry HM, Zhou N, Rickett DV, Baxter CJ, Enfissi EMA, Fraser PD (2023) The characterisation of phytoene synthase-1 and 2, and 1-D-deoxy-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase genes from red chilli pepper ( Capsicum annuum ). The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology 98: 732–744
Bohinc K, Lasić P, Matijaković Mlinarić N, Šupljika F, Smolič B, Abram A, Jerman I, Van De Velde NW, Mencin M, Kralj MB, et al (2024) The Biophysical Properties of the Fruit Cuticles of Six Pear Cultivars during Postharvest Ripening. Agronomy 14: 496
Carmona L, Sulli M, Diretto G, Alquézar B, Alves M, Peña L (2022) Improvement of Antioxidant Properties in Fruit from Two Blood and Blond Orange Cultivars by Postharvest Storage at Low Temperature. Antioxidants 11: 547
Chigwaya K, Karuppanapandian T, Schoeman L, Viljoen DW, Crouch IJ, Nugraha B, Verboven P, Nicolaï BM, Crouch EM (2021) X-ray CT and porosity mapping to determine the effect of ‘Fuji’ apple morphological and microstructural properties on the incidence of CO2 induced internal browning. Postharvest Biology and Technology 174: 111464
Chirinos X, Ying S, Rodrigues MA, Maza E, Djari A, Hu G, Liu M, Purgatto E, Fournier S, Regad F, et al (2023) Transition to ripening in tomato requires hormone-controlled genetic reprogramming initiated in gel tissue. Plant Physiology 191: 610–625
Dono G, Rambla JL, Frusciante S, Granell A, Diretto G, Mazzucato A (2020) Color Mutations Alter the Biochemical Composition in the San Marzano Tomato Fruit. Metabolites 10: 110
Geldhof B, Novák O, Van De Poel B (2024) Leaf ontogeny modulates epinasty through shifts in hormone dynamics during waterlogging in tomato. Journal of Experimental Botany 75: 1081–1097
Geldhof B, Pattyn J, Mohorović P, Van Den Broeck K, Everaerts V, Novák O, Van De Poel B (2022) Leaf ontogeny steers ethylene and auxin crosstalk to regulate leaf epinasty during waterlogging of tomato. doi: 10.1101/2022.12.02.518836
Geldhof B, Pattyn J, Van De Poel B (2023) From a different angle: genetic diversity underlies differentiation of waterlogging-induced epinasty in tomato. Front Plant Sci 14: 1178778
Gianoglio S, Comino C, Moglia A, Acquadro A, García-Carpintero V, Diretto G, Sevi F, Rambla JL, Dono G, Valentino D, et al (2022) In-Depth Characterization of greenflesh Tomato Mutants Obtained by CRISPR/Cas9 Editing: A Case Study With Implications for Breeding and Regulation. Front Plant Sci 13: 936089
Gómez-Gómez L, Morote L, Fajardo CM, Rubio-Moraga Á, Frusciante S, Diretto G, Ahrazem O (2023) Engineering the production of crocins and picrocrocin in heterologous plant systems. Industrial Crops and Products 194: 116283
Hasnaoui SE, Fahr M, Zouine M, Smouni A (2022) De Novo Transcriptome Assembly, Gene Annotations, and Characterization of Functional Profiling Reveal Key Genes for Lead Alleviation in the Pb Hyperaccumulator Greek Mustard (Hirschfeldia incana L.). CIMB 44: 4658–4675
Holden AC, Cohen H, Berry HM, Rickett DV, Aharoni A, Fraser PD (2024) Carotenoid retention during post-harvest storage of Capsicum annuum : the role of the fruit surface structure. Journal of Experimental Botany 75: 1997–2012
Konkina A, Klepadlo M, Lakehal A, Zein ZE, Krokida A, Botros M, Iakovidis M, Chernobavskiy P, Elfatih Zerroumda M, Tsanakas G, et al (2021) An Arabidopsis Prolyl 4 Hydroxylase Is Involved in the Low Oxygen Response. Front Plant Sci 12: 637352
Leszczuk A, Kalaitzis P, Blazakis KN, Zdunek A (2020) The role of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) in fruit ripening—a review. Hortic Res 7: 176
Leszczuk A, Kalaitzis P, Kulik J, Zdunek A (2023) Review: structure and modifications of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs). BMC Plant Biol 23: 45
Mellidou I, Koukounaras A, Frusciante S, Rambla JL, Patelou E, Ntoanidou S, Pons C, Kostas S, Nikoloudis K, Granell A, et al (2023) A metabolome and transcriptome survey to tap the dynamics of fruit prolonged shelf-life and improved quality within Greek tomato germplasm. Front Plant Sci 14: 1267340
Mellidou I, Koukounaras A, Kostas S, Patelou E, Kanellis AK (2021) Regulation of Vitamin C Accumulation for Improved Tomato Fruit Quality and Alleviation of Abiotic Stress. Genes 12: 694
Milutinović M, Nakarada Đ, Božunović J, Todorović M, Gašić U, Živković S, Skorić M, Ivković Đ, Savić J, Devrnja N, et al (2023) Solanum dulcamara L. Berries: A Convenient Model System to Study Redox Processes in Relation to Fruit Ripening. Antioxidants 12: 346
Modesti M, Forniti R, Brunori E, Mencarelli F, Bellincontro A, Tonutti P (2022) Ozone treatments to induce systemic-acquired resistance in leaves of potted vines: molecular responses and NIR evaluation for identifying effective dose and exposition duration. OENO One 56: 175–187
Modesti M, Marchica A, Pisuttu C, Risoli S, Pellegrini E, Bellincontro A, Mencarelli F, Tonutti P, Nali C (2023) Ozone-Induced Biochemical and Molecular Changes in Vitis vinifera Leaves and Responses to Botrytis cinerea Infections. Antioxidants 12: 343
Morote L, Lobato-Gómez M, Ahrazem O, Argandoña J, Olmedilla-Alonso B, López-Jiménez AJ, Diretto G, Cuciniello R, Bergamo P, Frusciante S, et al (2023) Crocins-rich tomato extracts showed enhanced protective effects in vitro. Journal of Functional Foods 101: 105432
Nogueira M, Enfissi EMA, Price EJ, Menard GN, Venter E, Eastmond PJ, Bar E, Lewinsohn E, Fraser PD (2024) Ketocarotenoid production in tomato triggers metabolic reprogramming and cellular adaptation: The quest for homeostasis. Plant Biotechnology Journal 22: 427–444
Rabasovic MS, Marinkovic BP, Rabasovic MD, Nikolic MG, Sevic D (2021) Time-resolved luminescence spectra of greater celandine plant extract (Chelidonium majus L.). Eur Phys J D 75: 180
Rodríguez-Lorenzo M, Mauri N, Royo C, Rambla JL, Diretto G, Demurtas O, Hilbert G, Renaud C, Tobar V, Huete J, et al (2023) The flavour of grape colour: anthocyanin content tunes aroma precursor composition by altering the berry microenvironment. Journal of Experimental Botany 74: 6369–6390
Salamé E, Brizzolara S, Rodriguez M, Iob M, Tonutti P, Ruperti B (2023) Ethanol fermentation- and ethylene physiology-related gene expression profiles in Red Delicious apples stored under variable hypoxic conditions and protocols. Adv Hort Sci 37: 89–99
Shiriaev A, Brizzolara S, Sorce C, Meoni G, Vergata C, Martinelli F, Maza E, Djari A, Pirrello J, Pezzarossa B, et al (2023) Selenium Biofortification Impacts the Tomato Fruit Metabolome and Transcriptional Profile at Ripening. J Agric Food Chem 71: 13554–13565
Silva A, Noronha H, Ricci D, Frusciante S, Diretto G, Conde C, Granell A, Gerós H (2023) Role in Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis of the Grapevine Plastidic Phosphoenolpyruvate Translocator VviPPT1. J Plant Growth Regul. doi: 10.1007/s00344-023-11127-4
Teixeira A, Noronha H, Frusciante S, Diretto G, Gerós H (2023) The grapevine metabolite profile of phloem sap is modified by flavescence dorée. OENO One 57: 307–320
Ustun H, Dogan A, Peker B, Ural C, Cetin M, Ozyigit Y, Erkan M (2023) Determination of the relationship between respiration rate and ethylene production by fruit sizes of different tomato types. J Sci Food Agric 103: 176–184
Villano C, Demurtas OC, Esposito S, Granell A, Rambla JL, Piombino P, Frusciante L, Carputo D, Diretto G, Aversano R (2023) Integrative analysis of metabolome and transcriptome profiles to highlight aroma determinants in Aglianico and Falanghina grape berries. BMC Plant Biol 23: 241
- A xanthophyll-derived apocarotenoid regulates carotenogenesis in tomato chromoplasts. 2023 - Plant Science Volume 328, March 2023, 111575 - https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2022.111575
- Determination of the relationship between respiration rate and ethylene production by fruit sizes of different tomato types. J Sci Food Agric. 2023 Jan 15;103(1):176-184. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12129.
- Biosynthesis of Chlorophyll and Other Isoprenoids in the Plastid of Red Grape Berry Skins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2023 71 (4), 1873-1885. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07207
- Engineering the production of crocins and picrocrocin in heterologous plant systems, Industrial Crops and Products, Volume 194, 2023, 116283, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.116283.
- Ozone-Induced Biochemical and Molecular Changesin Vitis vinifera Leaves and Responses to Botrytis cinerea Infections. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 343.
- Review: structure and modifications of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs). BMC Plant Biology volume 23, Article number: 45 (2023)
- Transition to ripening in tomato fruit needs genetic reprogramming initiated in gel tissue under multi-hormonal control – 2023 – Plant Physiology
- De Novo Transcriptome Assembly, Gene Annotations, and Characterization of Functional Profiling Reveal Key Genes for Lead Alleviation in the Pb Hyperaccumulator Greek Mustard (Hirschfeldia incana L.) – 2022 – Current issues in Molecular Biology
- Determination of the relationship between respiration rate and ethylene production by fruit sizes of different tomato types – 2022 - J Sci Food Agric
- Response of prolyl 4 hydroxylases, Arabinogalactan proteins and pectins content under long salinity stress in four olive cultivars – 2022 – Cells
- Arabinogalactan protein is a molecular and cytological marker of particular stages of the fruit ripening process (submitted)
- An Arabidopsis Prolyl 4 Hydroxylase Is Involved in the Low Oxygen Response – 2021 - Front. Plant Sci.
- Time-resolved luminescence spectra of greater celandine plant extract (Chelidonium majus L.) – 2021 - The European Physical Journal
- X-ray CT and porosity mapping to determine the effect of ‘Fuji’ apple morphological and microstructural properties on the incidence of CO2 induced internal browning – 2021 - Postharvest Biology and Technology
- The role of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) in fruit ripening – 2020 – Horticulture Research
- Ahrazem et al., 2022. Engineering high levels of saffron apocarotenoids in tomato. Horticulture Research, 9: uhac074; https://doi.org/10.1093/hr/uhac074
- Dono et al., 2022. Color Mutations Alter the Biochemical Composition in the San Marzano Tomato Fruit. Horticulturae, 8, 120; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10030110
In-Depth Characterization of greenflesh Tomato Mutants Obtained by CRISPR/Cas9 Editing: A Case Study With Implications for Breeding and Regulation.
 Gene editing has already proved itself as an invaluable tool for the generation of mutants for crop breeding, yet its ultimate impact on agriculture will depend on how crops generated by gene editing technologies are regulated, and on our ability to characterize the impact of mutations on plant phenotype. A starting operational strategy for evaluating gene editing-based approaches to plant breeding might consist of assessing the effect of the induced mutations in a crop- and locus-specific manner: this involves the analysis of editing efficiency in different cultivars of a crop, the assessment of potential off-target mutations, and a phenotypic evaluation of edited lines carrying different mutated alleles. Here, we targeted the GREENFLESH (GF) locus in two tomato cultivars (‘MoneyMaker’ and ‘San Marzano’) and evaluated the efficiency, specificity and mutation patterns associated with CRISPR/Cas9 activity for this gene. The GF locus encodes a Mg-dechelatase responsible for initiating chlorophyll degradation; in gf mutants, ripe fruits accumulate both carotenoids and chlorophylls. Phenotypic evaluations were conducted on two transgene-free T2 ‘MoneyMaker’ gf lines with different mutant alleles (a small insertion of 1 nucleotide and a larger deletion of 123 bp). Both lines, in addition to reduced chlorophyll degradation, showed a notable increase in carotenoid and tocopherol levels during fruit ripening. Infection of gf leaves and fruits with Botrytis cinerea resulted in a significant reduction of infected area and pathogen proliferation compared to the wild type (WT). Our data indicates that the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutation of the GF locus in tomato is efficient, specific and reproducible and that the resulting phenotype is robust and consistent with previously characterized greenflesh mutants obtained with different breeding techniques, while also shedding light on novel traits such as vitamin E overaccumulation and pathogen resistance. This makes GF an appealing target for breeding tomato cultivars with improved features for cultivation, as well as consumer appreciation and health.
Gene editing has already proved itself as an invaluable tool for the generation of mutants for crop breeding, yet its ultimate impact on agriculture will depend on how crops generated by gene editing technologies are regulated, and on our ability to characterize the impact of mutations on plant phenotype. A starting operational strategy for evaluating gene editing-based approaches to plant breeding might consist of assessing the effect of the induced mutations in a crop- and locus-specific manner: this involves the analysis of editing efficiency in different cultivars of a crop, the assessment of potential off-target mutations, and a phenotypic evaluation of edited lines carrying different mutated alleles. Here, we targeted the GREENFLESH (GF) locus in two tomato cultivars (‘MoneyMaker’ and ‘San Marzano’) and evaluated the efficiency, specificity and mutation patterns associated with CRISPR/Cas9 activity for this gene. The GF locus encodes a Mg-dechelatase responsible for initiating chlorophyll degradation; in gf mutants, ripe fruits accumulate both carotenoids and chlorophylls. Phenotypic evaluations were conducted on two transgene-free T2 ‘MoneyMaker’ gf lines with different mutant alleles (a small insertion of 1 nucleotide and a larger deletion of 123 bp). Both lines, in addition to reduced chlorophyll degradation, showed a notable increase in carotenoid and tocopherol levels during fruit ripening. Infection of gf leaves and fruits with Botrytis cinerea resulted in a significant reduction of infected area and pathogen proliferation compared to the wild type (WT). Our data indicates that the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutation of the GF locus in tomato is efficient, specific and reproducible and that the resulting phenotype is robust and consistent with previously characterized greenflesh mutants obtained with different breeding techniques, while also shedding light on novel traits such as vitamin E overaccumulation and pathogen resistance. This makes GF an appealing target for breeding tomato cultivars with improved features for cultivation, as well as consumer appreciation and health.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.936089
Improvement of Antioxidant Properties in Fruit from Two Blood and Blond Orange Cultivars by Postharvest Storage at Low Temperature
 Numerous studies have revealed the remarkable health-promoting activities of citrus fruits, all of them related to the accumulation of bioactive compounds, including vitamins and phytonutrients. Anthocyanins are characteristic flavonoids present in blood orange, which require low-temperature for their production. Storage at low-temperature of blood oranges has been proven to be a feasible postharvest strategy to increase anthocyanins in those countries with warm climates. To our knowledge, no studies comparing the effect of postharvest storage effect on phenylpropanoid accumulation in cultivars with and without anthocyanins production have been published. We have investigated the effect of postharvest cold storage in flavonoid accumulation in juice from Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck in two different oranges: Pera, a blond cultivar, and Moro, a blood one. Our findings indicate a different response to low-temperature of fruit from both cultivars at biochemical and molecular levels. Little changes were observed in Pera before and after storage, while a higher production of phenylpropanoids (3.3-fold higher) and flavonoids (1.4-fold higher), including a rise in anthocyanins from 1.3 ± 0.7 mg/L to 60.0 ± 9.4 mg/L was observed in Moro concurrent with an upregulation of the biosynthetic genes across the biosynthetic pathway. We show that postharvest storage enhances not only anthocyanins but also other flavonoids accumulation in blood oranges (but not in blond ones), further stimulating the interest in blood orange types in antioxidant-rich diets.
Numerous studies have revealed the remarkable health-promoting activities of citrus fruits, all of them related to the accumulation of bioactive compounds, including vitamins and phytonutrients. Anthocyanins are characteristic flavonoids present in blood orange, which require low-temperature for their production. Storage at low-temperature of blood oranges has been proven to be a feasible postharvest strategy to increase anthocyanins in those countries with warm climates. To our knowledge, no studies comparing the effect of postharvest storage effect on phenylpropanoid accumulation in cultivars with and without anthocyanins production have been published. We have investigated the effect of postharvest cold storage in flavonoid accumulation in juice from Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck in two different oranges: Pera, a blond cultivar, and Moro, a blood one. Our findings indicate a different response to low-temperature of fruit from both cultivars at biochemical and molecular levels. Little changes were observed in Pera before and after storage, while a higher production of phenylpropanoids (3.3-fold higher) and flavonoids (1.4-fold higher), including a rise in anthocyanins from 1.3 ± 0.7 mg/L to 60.0 ± 9.4 mg/L was observed in Moro concurrent with an upregulation of the biosynthetic genes across the biosynthetic pathway. We show that postharvest storage enhances not only anthocyanins but also other flavonoids accumulation in blood oranges (but not in blond ones), further stimulating the interest in blood orange types in antioxidant-rich diets.
Carmona, L.; Sulli, M.; Diretto, G.; Alquézar, B.; Alves, M.; Peña, L. Improvement of Antioxidant Properties in Fruit from Two Blood and Blond Orange Cultivars by Postharvest Storage at Low Temperature. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030547
Solanum dulcamara L. Berries: A Convenient Model System to Study Redox Processes in Relation to Fruit Ripening
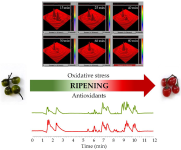 The present study provides, for the first time, a physicochemical and biochemical characterization of the redox processes associated with the ripening of Solanum dulcamara L. (bittersweet) berries. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (EPRS) and Imaging (EPRI) measurements of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were performed in parallel with the tissue-specific metabolic profiling of major antioxidants and assessment of antioxidant enzymes activity.
The present study provides, for the first time, a physicochemical and biochemical characterization of the redox processes associated with the ripening of Solanum dulcamara L. (bittersweet) berries. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (EPRS) and Imaging (EPRI) measurements of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were performed in parallel with the tissue-specific metabolic profiling of major antioxidants and assessment of antioxidant enzymes activity.
Milutinović, M.; Nakarada, Đ.; Božunović, J.; Todorović, M.; Gašić, U.; Živković, S.; Skorić, M.; Ivković, Đ.; Savić, J.; Devrnja, N.; Aničić, N.; Banjanac, T.; Mojović, M.; Mišić, D. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 346.
https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020346
Regulation of Vitamin C Accumulation for Improved Tomato Fruit Quality and Alleviation of Abiotic Stress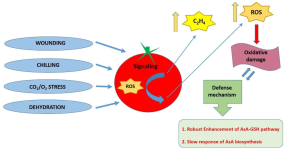
Considering the recent advances in our understanding of AsA regulation in model and other non-model species, this review attempts to link the current consensus with novel technologies to provide a comprehensive strategy for AsA enhancement in tomatoes, without any detrimental effect on plant growth or fruit development.
Mellidou I, Koukounaras A, Kostas S, Patelou E, Kanellis AK.
Genes (Basel). 2021 May 6;12(5):694.
https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12050694
Time-resolved luminescence spectra of greater celandine plant extract (Chelidonium majus L.)
In this work, we analyze optical characteristics of greater celandine (Chelidonium majus L.) ethanol solution extracts and fresh leaf samples. Optical emission of samples
was measured using a pulsed laser excitation of tunable wavelengths (320–470 nm) and time-resolved detection system. Results of our analysis reveal two distinct alkaloid optical emission bands with different excitation characteristics. Chlorophyll fluorescence emission band was also detected. Time-resolved analysis of luminescent spectra shows that lifetimes of both alkaloid fluorescence bands and chlorophyll band are in nanosecond domain.
M. S. Rabasovica, B. P. Marinkovic , M. D. Rabasovic , M. G. Nikolic, and D. Sevic
Eur. Phys. J. D (2021) 75: 180
https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00185-6
An Arabidopsis Prolyl 4 Hydroxylase Is Involved in the Low Oxygen Response
Plant responses to flooding, submergence and waterlogging are important for adaptation to climate chang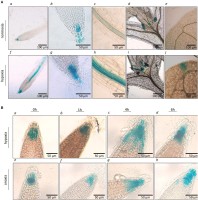 e environments. Therefore, the characterization of the molecular mechanisms activated under hypoxic and anoxic conditions might lead to low oxygen resilient crops. Although in mammalian systems prolyl 4 hydroxylases (P4Hs) are involved in the oxygen sensing pathway, their role in plants under low oxygen has not been extensively investigated. In this report, an Arabidopsis AtP4H3 T-DNA knock out mutant line showed higher sensitivity to anoxic treatment possibly due to lower induction of the fermentation pathway genes, ADH and PDC1, and of sucrose synthases, SUS1 and SUS4. This sensitivity to anoxia was accompanied by lower protein levels of AGPs-bound epitopes such as LM14 in the mutant line and induction of extensins-bound epitopes, while the expression levels of the majority of the AGPs genes were stable throughout a low oxygen time course. The lower AGPs content might be related to altered frequency of proline hydroxylation occurrence in the p4h3 line. These results indicate active involvement of proline hydroxylation, a post-translational modification, to low oxygen response in Arabidopsis.
e environments. Therefore, the characterization of the molecular mechanisms activated under hypoxic and anoxic conditions might lead to low oxygen resilient crops. Although in mammalian systems prolyl 4 hydroxylases (P4Hs) are involved in the oxygen sensing pathway, their role in plants under low oxygen has not been extensively investigated. In this report, an Arabidopsis AtP4H3 T-DNA knock out mutant line showed higher sensitivity to anoxic treatment possibly due to lower induction of the fermentation pathway genes, ADH and PDC1, and of sucrose synthases, SUS1 and SUS4. This sensitivity to anoxia was accompanied by lower protein levels of AGPs-bound epitopes such as LM14 in the mutant line and induction of extensins-bound epitopes, while the expression levels of the majority of the AGPs genes were stable throughout a low oxygen time course. The lower AGPs content might be related to altered frequency of proline hydroxylation occurrence in the p4h3 line. These results indicate active involvement of proline hydroxylation, a post-translational modification, to low oxygen response in Arabidopsis.
Konkina A, Klepadlo M, Lakehal A, Zein ZE, Krokida A, Botros M, Iakovidis M, Chernobavskiy P, Elfatih Zerroumda M, Tsanakas G, Petrakis N, Dourou AM, Kalaitzis P. An Arabidopsis Prolyl 4 Hydroxylase Is Involved in the Low Oxygen Response. Front Plant Sci. 2021 Mar 15;12:637352.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2021.637352/full
The role of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) in fruit ripening—a review
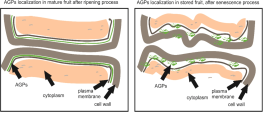
In this review, authors summarise the results of pioneering studies on Arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) in fruit tissue with their structure, specific localization pattern, stress factors influencing their presence, and a focus on recent advances.
Leszczuk, A., Kalaitzis, P., Blazakis, K.N. et al. The role of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) in fruit ripening—a review. Hortic Res 7, 176 (2020).


